Myofascial Release: What It Is And What Are Its Benefits
Mobility problems and pain are prevented with myofascial release therapies, a technique that addresses specific areas of the body surrounded by fasciae.
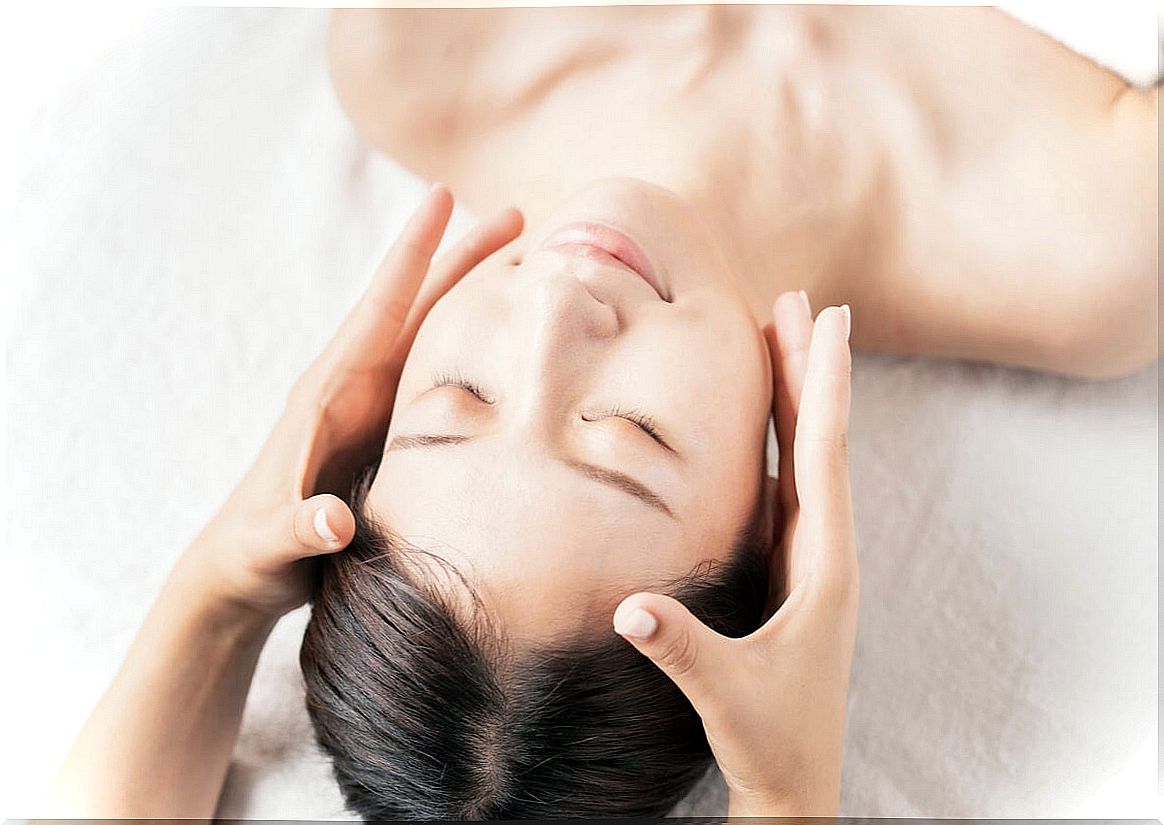

Myofascial release relieves pain after injury. It is based on manual massages that stimulate the affected area and achieve the movement of muscle fasciae that are under the skin.
It is also known as myofascial induction and is applied by physiotherapists or masseurs to regain the functionality of the tissues. It directly affects the locomotor system and extends to the rest of the body, calming the discomfort through pressure and stretching.
What is myofascial release?
Before explaining the technique it is necessary to know what a fascia is. It is the tissue that surrounds muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics and viscera, in addition to connecting the organs allowing biomechanical activity.
According to an article published in the Cuban Journal of Biomedical Research, myofascia facilitates mobility, cellular circulation and the elasticity of tissues in the face of stress spasms, injuries and inactivity. This leads to pain points that, if not addressed, would be chronic.
Faced with this diagnosis, specialists appeal to myofascial release therapies, because they mechanically activate the tissue to release tension and calm discomfort, both in the specific area and in remote areas.
Pressures are sustained and light, as is stretching and movement. The goal is to remove functional restrictions thanks to the stimulation of collagen and its properties.
Parts of the body that are treated with the technique
Myofascial induction is used to manage the numbness of parts that remain fixed for a long time or that we use frequently, such as the head, jaw, neck, quadriceps, arms, back, hips, feet and calves .
It happens that many joint or muscle pains are the result of injuries, busyness or the rhythm of life. Similarly, they are associated with physiological movements that go unnoticed, such as lung expansion when we breathe.
With it fibromyalgias, lumbago, migraines, tendinitis, post-traumatic and postsurgical scars, stiffness due to neurological affectations, whiplash and chronic prostatitis are treated. However, it is not a first-line approach. It should always be a therapeutic complement to the specific medical prescription.
Benefits of myofascial release
The greatest benefit is optimal body mobility, due to relaxation at the trigger points. The technique keeps the body in good condition, there is better circulation and toxins are eliminated via the lymphatic ducts.
Other benefits of myofascial release are the following:
- Completely relax the body.
- The locomotor apparatus recovers its functionality.
- It alleviates the discomforts of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and scleroderma.
- Balances the musculoskeletal system.
- Extend the range of motion.
- Minimize tension and stress.
With fascial release therapies, relief is global. For this reason it is used as a complement for sports warm-ups together with the foam roller technique . They also offer it in physiotherapy rooms.
Contraindications of myofascial release
Before the sessions, the expert evaluates the patient to determine the exercises. But not everyone is a candidate for this treatment.
It is contraindicated in those who take anticoagulants or suffer from metabolic conditions, fractures, aneurysms and osteoporosis. Nor is it used if there are open wounds, burns, fever, infectious pathologies or state of pregnancy.
In addition to physiotherapy centers, myofascial release can be done at home with simple methods, always guided by a connoisseur of the subject. Although there are tutorials online, the right thing to do is to have a professional.
How do you do a session?
The sessions do not exceed 1 hour and consist of the steps explained below:
- Assessment: it is the static and dynamic test of the patient to verify the state of the fascial system and specify the alterations.
- Warm-up : with the fingers, palms and elbows the physiotherapist, masseuse or chiropractor prepares the fascia.
- Stretching: these are long, smooth and sustained manual movements that stretch and release the fascia without forcing it.
The techniques are superficial or deep. The former include J-slides that increase skin movement, transverse fiber slides, and longitudinal slides made with the fingers, elbows, or knuckles.
On the other hand, the deep ones are exerted in transverse planes, with crossed hands and in a craniosacral direction, that is, from the head to the feet.

What to keep in mind about myofascial induction
Myofascial induction is most effective when combined with neurodynamics, osteopathy, and global postural reeducation. The physical therapist will know which ones are suitable for your condition.
Likewise, it establishes the number of sessions according to the tension evidenced by the fascia, pain and trigger points. The frequency is a weekly and 6 in total. Each therapy lasts 1 hour, but if the pain is extreme, it may reach 3.
For greater effectiveness it is advisable to drink plenty of water. In the same way, remember that tensions or pain are not caused only by injuries; emotions, stress and trauma are also treated with this method.
This is not an aesthetic treatment, much less massage to shape the figure. Whoever applies it has to have the knowledge and carry it out in specialized clinics.









